Give before midnight on July 31 to double your impact where trees need us most. CHOOSE A PROJECT
Project
The Hybrid Hazelnut Consortium
Hazelnuts hold great promise for increasing the world’s sustainable food, feed, and energy supply. That’s why both researchers and members around the United States are working together to expand the potential of this hybrid crop.
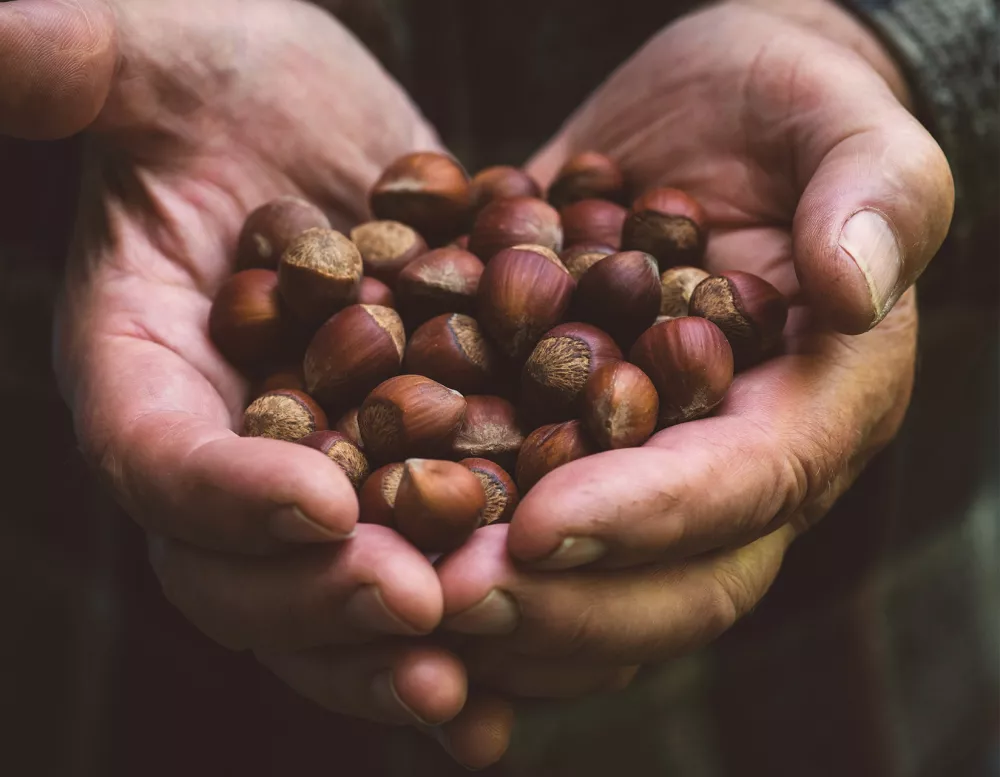

Creating a research and breeding program to develop hazelnuts as a widely adapted, high-yielding, and low-input sustainable crop that is competitive for food, feed, or bioenergy.
The consortium is comprised of four organizations dedicated to this goal: the Arbor Day Foundation, Oregon State University, Rutgers University, and the Nebraska Forest Service/University of Nebraska-Lincoln. The consortium has received $3.1 million from the USDA to continue its work on developing next-generation hybrids that can expand commercial hazelnut production in the U.S.
The Benefits of Hazelnuts
Nutrition
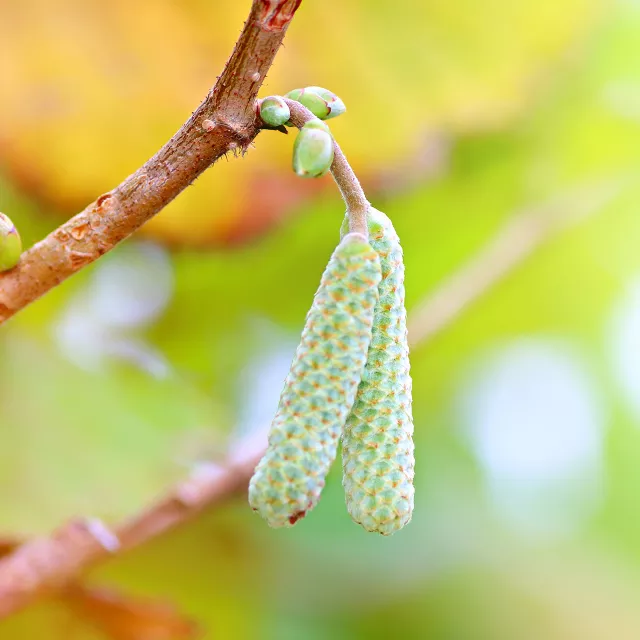

A Leader in Nutritional Qualities
Experts agree that hazelnuts are packed with vitamins, protein, and good fats, earning them the FDA heart healthy seal of approval. Hazelnuts rank at or near the top of many of the important health categories. Hazelnuts are a rich source of protein, vitamin E, folate, B vitamins, and arginine. Hazelnut cooking oil has a similar composition to extra virgin olive oil with high content in Omega 9 and Omega 6 fatty acid. This makes hazelnuts another healthy cooking oil option with flavorful taste. Hazelnuts have not yet reached their full potential in the United States. With much wider sustainable production, they could be a main component of a healthy diet.

Environmental & Agricultural Benefits
- Drought Resistance: Perennial plants' deep roots resist short-term droughts, unlike annual crops.
- Carbon Sequestration: Hazelnuts absorb more carbon than annual crops, aiding in carbon sequestration.
- Soil Erosion: Hazelnuts reduce erosion with minimal tillage and extended soil coverage as riparian buffer zone species.
- Nitrogen Leaching: Their active perennial roots minimize nitrogen leaching year-round.
- Land Diversification: Hazelnuts thrive on marginal soils and slopes, diversifying land use sustainably.

Sustainable Energy from Hazelnut Oil
Hazelnut oil is a largely unexplored, yet promising resource. Preliminary data reveals that opportunities exist to expand new markets for hazelnuts, such as for feed and biodiesel. Utilizing previous funding, the Hybrid Hazelnut Consortium has led the way in hazelnut oil research by investigating and enhancing the quantity of oil from hybrid hazelnuts while examining the properties of oil for both food oil and biofuel applications.

Wildlife Benefits from Hazelnuts Too
Hazelnut plants can provide great wildlife habitat and nutrition. In addition to the environmental benefits of hazelnuts, these bushes make attractive CRP plants, windbreaks, hedges, or riparian buffers.
Known wildlife that benefits from hazelnut plants include:
- Birds: Quail, Ruffed Grouse, Wild Turkey, Pheasants, Woodpeckers, Blue Jays
- Rodents: Squirrels, Chipmunks, Mice
- Large Animals: Ground Hogs, Deer

Hazelnuts as Animal Feed
Feedstock is a largely unexplored, yet promising, opportunity for hazelnuts. The high protein content in native hazelnuts already makes them an attractive wildlife and livestock feed.
Through the Consortium’s breeding process, we hope to increase the amount of protein that can be grown per acre. In addition, the adoption of hazelnuts as a widely grown feedstock crop would increase overall crop diversity, which reduces producer risk and promotes more integrated, environmentally friendly production systems.
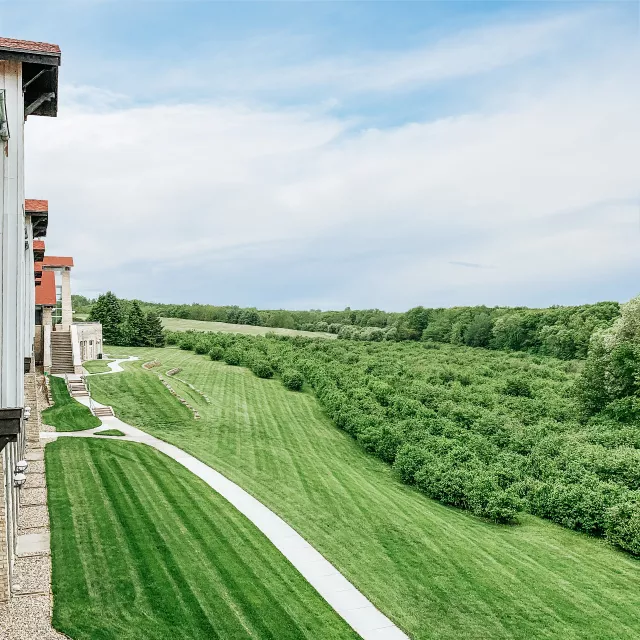

The Arbor Day Foundation's Role in the Hazelnut Consortium
The Arbor Day Foundation began the Hazelnut Research Project in 1996 with plantings of hybrid hazelnuts at Arbor Day Farm. By 2000 the project evolved to include charter members across the nation conducting research on hazelnuts in their own backyards and has nearly reached 100,000 active members. Key findings include:
- Best Practices and methods for growing hazelnuts from seeds.
- Hybrids Hazelnuts can thrive in Nebraska, among other states, as a dryland crop.
- Arbor Day Farm Hybrids grow best in zones 4 to 8.
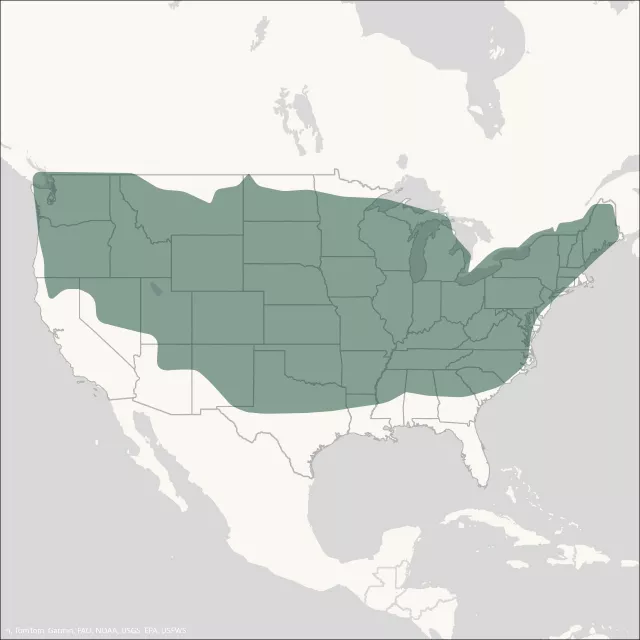
The Expansion of Hybrid Hazelnuts
The primary goal of the Hybrid Hazelnut Consortium is to significantly expand the commercial production region of hazelnuts in the United States and Canada. This goal can be met by focusing research and breeding efforts on developing productive hazelnut plants that express durable resistance to the disease Eastern Filbert Blight (EFB) while also enhancing cold hardiness and drought tolerance.
Members of the Consortium
Each member is playing a significant role in the research and development of hybrid hazelnuts.








The Consortium Timeline
In cooperation with Philip Rutter, a pioneer in hazelnut research and founder of Badgersett Research Corporation, 5,200 hazelnut bushes representing 60 promising hybrids replaced a cherry orchard and covered the slope behind Lied Lodge at Arbor Day Farm. In the following years, members received nuts from the orchard for planting in all kinds of conditions throughout the United States.
By 2005, the benefits of hazelnuts had touched the lives of 50,930 members who agreed to plant, observe, and report results. In return, participants received an annual report and Home Harvest Guide. On farms, in small towns, and in city suburbs, members found that participation was not only helpful, but interesting and fun. In some instances, it has also been financially rewarding—with crops available to sell or help feed the family.
Research scientists at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln, Rutgers University, and Oregon State University joined with Foundation staff to form the Hybrid Hazelnut Consortium. This expansion of expertise provided better opportunities to analyze reports from members, screen for the best bushes, and reproduce progeny through state-of-the-art laboratory and nursery techniques.
Using nuts from the best of the original plants returned by patrons, along with promising bushes discovered growing in the wild, new seedlings were propagated and planted in the orchard at Arbor Day Farm. This introduction into the orchard not only provided nuts for further distribution and testing, but provided additional diversity that should lead to even better hybrids in the future.
The Hybrid Hazelnut Consortium secured a 5-year grant totaling $3.1 million from the USDA to continue its work on developing a next-generation hybrid that can expand commercial hazelnut production in the U.S. This funding was made available due to the progress the consortium has made so far—with critical support from Hazelnut Project Charter Patrons who have planted hybrid hazelnuts and reported their results.

How to Find Hazelnuts
Native American Hazelnuts are found in the midwestern, eastern, and southeastern regions of the United States and in Canada. Please refer to the map to discover if you might have American hazelnuts growing in your state. The Consortium is primarily seeking samples from Alabama, Arkansas, Kentucky, Missouri, North and South Carolina, and Tennessee, especially in higher elevations in these states.
- Heart-Shaped Leaves (paler on the back than the front)
- Involucre (leafy bract)
- 8-to-15 FT Tall Shrub
- Hazelnut Nut
- Catskins






